You’re Not “Bad at Prompts”—You’re Just Using the Wrong System
Table of Contents
Open your notes app. If it’s full of random snippets like “write an email,” “generate SEO keywords,” “make it sound human,” you’re not alone.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!But here’s the brutal truth:
Prompt collecting feels productive. It’s not.
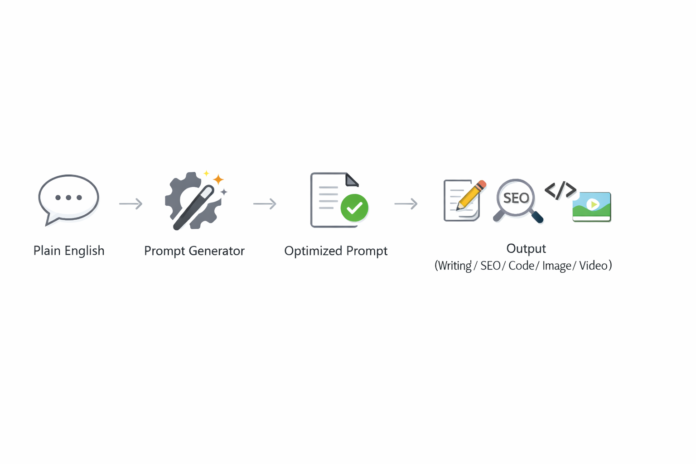
What you actually want is ChatGPT prompt engineering that works like a master key—one method that reliably turns plain English into a precise, reusable prompt that fits the task.
Turn plain English into pro-level prompting. That’s the whole game.
Stop collecting prompts. Start collecting systems.
If you’ve ever read OpenAI’s own prompt engineering guidance, the theme is consistent: be clear, specific, provide structure, and iterate.
Google’s Gemini prompting guidance echoes the same fundamentals—clear goals, context, and constraints.
Now let’s turn those fundamentals into a “7 ways” playbook you can actually use.
Why “Prompt Collecting” Secretly Wastes Your Time
Prompt collecting fails for one annoying reason: prompts don’t transfer well.
A prompt that crushes email writing won’t automatically crush image prompts. A prompt that works in ChatGPT may need tweaks for Gemini. You end up with:
- 47 half-working templates
- inconsistent outputs
- constant re-editing
- and the creeping feeling that AI is “unreliable”
The fix is not “more templates.” The fix is better ChatGPT prompt engineering—a repeatable structure that adapts.
Pattern interrupt: If your prompt needs luck, it’s not a prompt. It’s a lottery ticket.
Way #1 — Use a Prompt Generator Prompt (Your “Master Key”)
This is the fastest upgrade you’ll ever make: use ChatGPT to write your prompts.
Create a “Prompt Generator” prompt that converts your messy idea into a polished, copy-paste prompt.
Copy-paste Prompt Generator (Master Key):
- Role: You are an Expert Prompt Architect and Prompt Engineer.
- Task: Convert my requirement into a highly detailed, optimized, ready-to-use prompt for the correct output type (writing/SEO/coding/image/video/research).
- Rules:
- Do not ask questions unless my request is unclear.
- Add missing but useful details (tone, style, constraints, structure).
- Include an explicit output format and quality checklist.
- Deliverables:
- Optimized Prompt (copy-paste ready)
- Optional Enhancers (short add-ons I can toggle)
USER REQUIREMENT: [paste your plain English here]
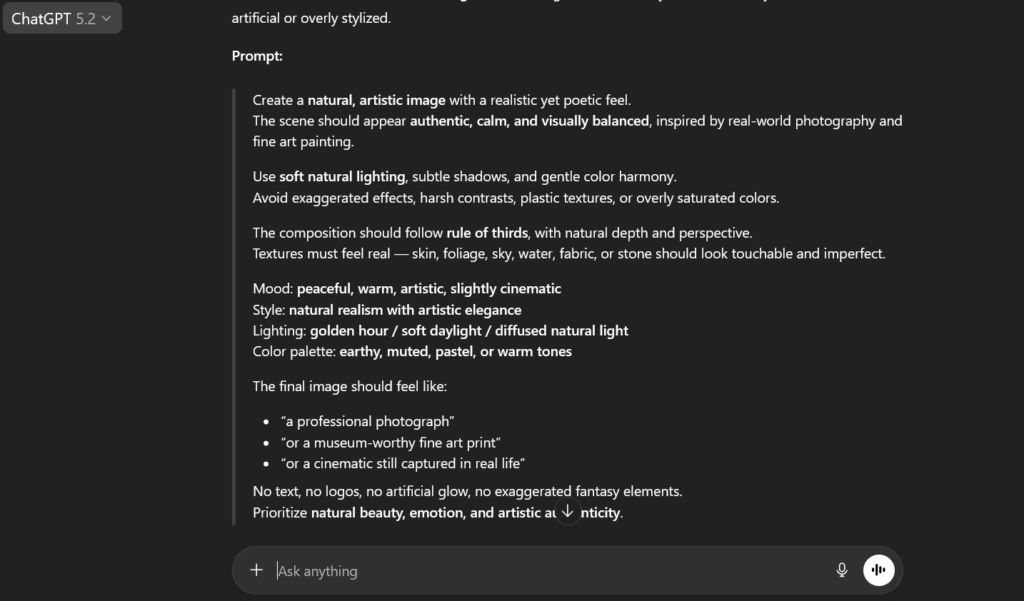
Below is the output of the generated prompt, from OpenAI.
This single move turns ChatGPT prompt engineering from “guess and hope” into “specify and win.”
Way #2 — Declare the Role, Then Lock the Job
Models behave differently depending on the “hat” you give them.
Instead of:
“Write a LinkedIn post.”
Try:
“You are a B2B SaaS copywriter. Write a LinkedIn post…”
Then lock the job with specifics:
- target reader (founder, recruiter, student)
- goal (educate, persuade, entertain)
- voice (punchy, calm, contrarian)
- angle (fear of missing out, step-by-step, myth-busting)
OpenAI explicitly recommends clear instructions and structured prompting to improve outcomes.
Mini checklist (30 seconds):
- Who are you? (role)
- What are you doing? (task)
- Who is it for? (audience)
- What does “good” look like? (criteria)
That’s ChatGPT prompt engineering with guardrails.
Way #3 — Demand an Output Format the Model Can’t Wiggle Out Of
If you don’t define the output, the model will improvise.
And improvisation is where quality goes to die.
Add hard formatting like:
- word count range
- headings
- bullet points
- JSON blocks
- tables (if needed)
- “return ONLY the final answer”
Gemini’s prompt strategy docs and Google’s Workspace tips both emphasize clarity and structured requests.
Example (format lock):
“Output exactly:
- Hook (2 lines)
- 7 bullets (no more than 12 words each)
- CTA (1 line)
No extra commentary.”
If you don’t choose the format, the model will choose chaos.
Way #4 — Add Constraints That Force Quality (Length, Tone, Audience)
Constraints sound limiting. They’re not.
They’re how you turn ChatGPT prompt engineering into a predictable machine.
Use constraint “packs” like:
- Length: “800–1,200 words. Short paragraphs (2–3 lines).”
- Tone: “Direct, practical, no hype, friendly confidence.”
- Reading level: “Explain like I’m smart but new.”
- Bans: “No clichés. No ‘In today’s world.’ No filler.”
- Quality bar: “Assume this will be published to a large audience.”
Want less fluff? Constraint-based prompting is a known tactic for controlling verbosity and output shape.
Pattern interrupt: Constraints don’t reduce creativity—they reduce mistakes.
Way #5 — Feed the Model Reference Text Like a Pro
The jump from “pretty good” to “wow” often comes from reference.
You can paste:
- your draft
- competitor sections
- product notes
- customer reviews
- meeting transcript highlights
Then instruct:
“Use ONLY the reference. If information is missing, say so. Don’t guess.”
This aligns with common best practices in prompt engineering: provide reference text and clear boundaries.
Example (reference-based prompt):
“Here is reference text: [PASTE]
Task: Write a 6-part email sequence.
Rules: Only use facts from the reference. Keep each email under 180 words. Add one curiosity hook per email.”
This is ChatGPT prompt engineering that reduces hallucinations and increases relevance.
Way #6 — Build a Two-Pass System: Draft → Critique → Final
Most people ask for “the final” too early.
Instead, do two passes:
- Draft quickly
- Critique hard (as an editor)
- Rewrite clean
Two-pass prompt template:
- Pass 1: “Create a draft that prioritizes speed.”
- Pass 2: “Now act as a ruthless editor. List 10 specific improvements.”
- Pass 3: “Rewrite implementing every improvement.”
OpenAI’s prompting guidance emphasizes iteration and refining prompts to improve results.
The first draft is what the model can do. The second draft is what you asked it to do.
Way #7 — Create a Reusable Prompt Library That Isn’t a Mess
Yes, you can keep templates—just don’t keep random ones.
Build a tiny library of prompt components, not full prompts:
A. Role blocks
- “You are a senior SEO strategist…”
- “You are a product UX writer…”
B. Output formats
- “Return: Title, Meta, Slug, Outline, Draft…”
C. Constraint packs
- “Short paragraphs, no fluff, actionable steps…”
D. Quality checklist
- “Include examples, edge cases, and a summary.”
Then you assemble them on demand—this is scalable ChatGPT prompt engineering.
Add internal placeholders so your blog/workflow benefits too:
- [Internal Link: /prompt-engineering-checklist/]
- [Internal Link: /best-chatgpt-workflows/]
- [Internal Link: /ai-writing-without-fluff/]
Pattern interrupt: Your “prompt library” should feel like LEGO, not a junk drawer.
Two credible resources to level up faster
If you want to anchor your practice in official guidance, these are worth keeping open while you experiment:
- OpenAI prompt engineering best practices and guides.
- Google Gemini prompt design strategies and prompting tips.
FAQ Section
1) What is ChatGPT prompt engineering?
ChatGPT prompt engineering is the practice of writing clear, structured instructions so ChatGPT produces outputs that match your goal, format, and quality standards.
2) How do I make ChatGPT write perfect prompts from plain English?
Use a “Prompt Generator” (master key) prompt that converts your requirement into an optimized, copy-paste prompt with role, constraints, and output format.
3) What’s the biggest mistake people make with ChatGPT prompt engineering?
They skip specificity—no role, no format, no constraints—then blame the model for “random” outputs.
4) Should I use one super prompt for everything?
Use one prompt generator for everything, yes. But the generated prompt should be tailored to the task (writing vs coding vs images).
5) How do I reduce fluff and over-explaining in responses?
Add strict constraints: length limits, “no background,” and a fixed output format (bullets, steps, or a short structure).
6) Does ChatGPT prompt engineering work the same for Gemini?
The fundamentals are similar—clarity, context, structure—but you may need small format tweaks depending on the tool’s behavior.
7) How many times should I iterate a prompt?
At least twice: Draft → Critique → Final. Iteration is where prompts become reliable.
Explore More from Tech Niche Pro
If you enjoyed this deep dive into Hybrid RAG, here are some other high-value guides from Tech Niche Pro that are worth your time:
— Build an AI Agent From Scratch in Python (No LangChain): Tools, Memory, Planning — In One Clean File — https://technichepro.com/build-an-ai-agent-from-scratch-python/
— The Next AI Boom: What’s Coming, Who Wins, and How to Prepare (2026 Edition) — https://technichepro.com/next-ai-boom-2026/
— Choose First AI Product: 10-Step Field Guide to a Useful AI App (2026) — https://technichepro.com/choose-first-ai-product-10-step-field-guide/
— AI Document Extraction: LLMs That Tame Complex PDFs — https://technichepro.com/ai-document-extraction-llms-that-tame-complex-pdfs/
Plus, for more AI trends, Python tutorials, and developer playbooks, browse the full archive at https://technichepro.com/ — your trusted source for real-world AI and tech insights.
These articles will help you extend your Python-AI skills, stay ahead in the AI revolution, and apply cutting-edge techniques to real-world problems.